xarray IRIS backend#
In this example, we read IRIS (sigmet) data files using the xradar iris xarray backend.
[1]:
import glob
import gzip
import io
import wradlib as wrl
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import xradar as xd
import datatree as xt
import xarray as xr
try:
get_ipython().run_line_magic("matplotlib inline")
except:
plt.ion()
/home/runner/micromamba/envs/wradlib-tests/lib/python3.11/site-packages/h5py/__init__.py:36: UserWarning: h5py is running against HDF5 1.14.3 when it was built against 1.14.2, this may cause problems
_warn(("h5py is running against HDF5 {0} when it was built against {1}, "
Load IRIS Volume Data#
[2]:
fpath = "sigmet/SUR210819000227.RAWKPJV"
f = wrl.util.get_wradlib_data_file(fpath)
vol = xd.io.open_iris_datatree(f, reindex_angle=False)
Downloading file 'sigmet/SUR210819000227.RAWKPJV' from 'https://github.com/wradlib/wradlib-data/raw/pooch/data/sigmet/SUR210819000227.RAWKPJV' to '/home/runner/work/wradlib/wradlib/wradlib-data'.
Inspect RadarVolume#
[3]:
display(vol)
<xarray.DatasetView>
Dimensions: ()
Data variables:
volume_number int64 0
platform_type <U5 'fixed'
instrument_type <U5 'radar'
time_coverage_start <U20 '2021-08-19T00:02:28Z'
time_coverage_end <U20 '2021-08-19T00:02:49Z'
longitude float64 25.52
altitude float64 157.0
latitude float64 58.48
Attributes:
Conventions: None
version: None
title: None
institution: None
references: None
source: None
history: None
comment: im/exported using xradar
instrument_name: NoneInspect root group#
The sweep dimension contains the number of scans in this radar volume. Further the dataset consists of variables (location coordinates, time_coverage) and attributes (Conventions, metadata).
[4]:
vol.root
[4]:
<xarray.DatasetView>
Dimensions: ()
Data variables:
volume_number int64 0
platform_type <U5 'fixed'
instrument_type <U5 'radar'
time_coverage_start <U20 '2021-08-19T00:02:28Z'
time_coverage_end <U20 '2021-08-19T00:02:49Z'
longitude float64 25.52
altitude float64 157.0
latitude float64 58.48
Attributes:
Conventions: None
version: None
title: None
institution: None
references: None
source: None
history: None
comment: im/exported using xradar
instrument_name: NoneInspect sweep group(s)#
The sweep-groups can be accessed via their respective keys. The dimensions consist of range and time with added coordinates azimuth, elevation, range and time. There will be variables like radar moments (DBZH etc.) and sweep-dependend metadata (like fixed_angle, sweep_mode etc.).
[5]:
display(vol["sweep_0"])
<xarray.DatasetView>
Dimensions: (azimuth: 359, range: 833)
Coordinates:
elevation (azimuth) float32 ...
time (azimuth) datetime64[ns] 2021-08-19T00:02:31.104000 .....
* range (range) float32 150.0 450.0 750.0 ... 2.494e+05 2.498e+05
longitude float64 ...
latitude float64 ...
altitude float64 ...
* azimuth (azimuth) float32 0.03021 1.035 2.054 ... 358.0 359.0
Data variables: (12/16)
DBTH (azimuth, range) float32 ...
DBZH (azimuth, range) float32 ...
VRADH (azimuth, range) float32 ...
WRADH (azimuth, range) float32 ...
ZDR (azimuth, range) float32 ...
KDP (azimuth, range) float32 ...
... ...
SNRH (azimuth, range) float32 ...
sweep_mode <U20 ...
sweep_number int64 ...
prt_mode <U7 ...
follow_mode <U7 ...
sweep_fixed_angle float64 ...Georeferencing#
[6]:
swp = vol["sweep_0"].ds.copy()
swp = swp.assign_coords(sweep_mode=swp.sweep_mode)
swp = swp.wrl.georef.georeference()
Inspect radar moments#
The DataArrays can be accessed by key or by attribute. Each DataArray has dimensions and coordinates of it’s parent dataset.
[7]:
display(swp.DBZH)
<xarray.DataArray 'DBZH' (azimuth: 359, range: 833)>
[299047 values with dtype=float32]
Coordinates: (12/15)
elevation (azimuth) float64 0.5054 0.5054 0.5054 ... 0.5054 0.5054 0.5054
time (azimuth) datetime64[ns] 2021-08-19T00:02:31.104000 ... 2021-...
* range (range) float32 150.0 450.0 750.0 ... 2.494e+05 2.498e+05
longitude float64 25.52
latitude float64 58.48
altitude float64 157.0
... ...
y (azimuth, range) float64 150.0 450.0 ... 2.493e+05 2.496e+05
z (azimuth, range) float64 158.3 161.0 ... 6.023e+03 6.034e+03
gr (azimuth, range) float64 150.0 450.0 ... 2.493e+05 2.496e+05
rays (azimuth, range) float32 0.03021 0.03021 0.03021 ... 359.0 359.0
bins (azimuth, range) float32 150.0 450.0 ... 2.494e+05 2.498e+05
crs_wkt int64 0
Attributes:
long_name: Equivalent reflectivity factor H
standard_name: radar_equivalent_reflectivity_factor_h
units: dBZCreate simple plot#
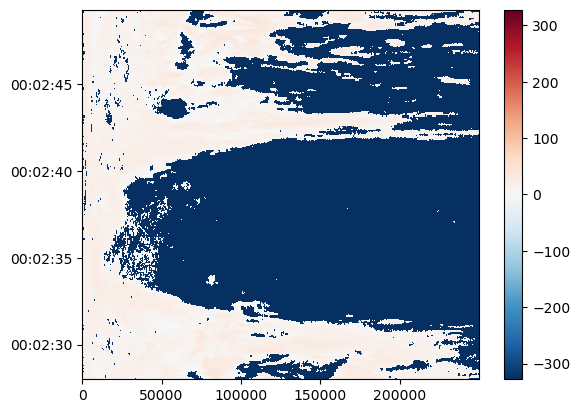
Using xarray features a simple plot can be created like this. Note the sortby('time') method, which sorts the radials by time.
For more details on plotting radar data see under Visualization.
[8]:
swp.DBZH.sortby("time").plot(x="range", y="time", add_labels=False)
[8]:
<matplotlib.collections.QuadMesh at 0x7f967380e950>
[9]:
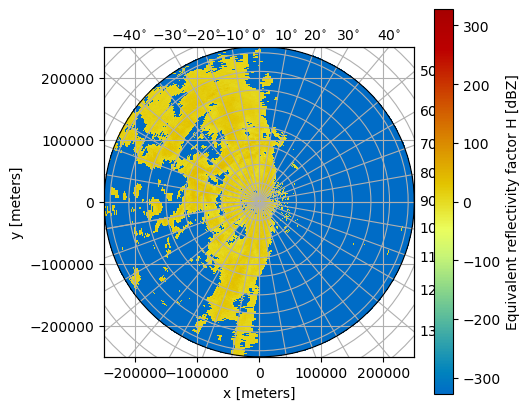
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(5, 5))
pm = swp.DBZH.wrl.vis.plot(crs={"latmin": 3e3}, fig=fig)
Retrieve explicit group#
[10]:
swp_b = xr.open_dataset(
f, engine="iris", group="sweep_0", backend_kwargs=dict(reindex_angle=False)
)
display(swp_b)
<xarray.Dataset>
Dimensions: (azimuth: 359, range: 833)
Coordinates:
elevation (azimuth) float32 ...
time (azimuth) datetime64[ns] ...
* range (range) float32 150.0 450.0 750.0 ... 2.494e+05 2.498e+05
longitude float64 ...
latitude float64 ...
altitude float64 ...
* azimuth (azimuth) float32 0.03021 1.035 2.054 ... 358.0 359.0
Data variables: (12/16)
DBTH (azimuth, range) float32 ...
DBZH (azimuth, range) float32 ...
VRADH (azimuth, range) float32 ...
WRADH (azimuth, range) float32 ...
ZDR (azimuth, range) float32 ...
KDP (azimuth, range) float32 ...
... ...
SNRH (azimuth, range) float32 ...
sweep_mode <U20 ...
sweep_number int64 ...
prt_mode <U7 ...
follow_mode <U7 ...
sweep_fixed_angle float64 ...