xarray Rainbow5 backend¶
In this example, we read Rainbow5 data files using the wradlib rainbow xarray backend.
[1]:
import glob
import gzip
import io
import wradlib as wrl
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
import matplotlib.pyplot as pl
import numpy as np
import xarray as xr
try:
get_ipython().run_line_magic("matplotlib inline")
except:
pl.ion()
/home/runner/micromamba-root/envs/wradlib-notebooks/lib/python3.11/site-packages/tqdm/auto.py:22: TqdmWarning: IProgress not found. Please update jupyter and ipywidgets. See https://ipywidgets.readthedocs.io/en/stable/user_install.html
from .autonotebook import tqdm as notebook_tqdm
Load Rainbow5 Volume Data¶
[2]:
fpath = "rainbow/2013051000000600dBZ.vol"
f = wrl.util.get_wradlib_data_file(fpath)
vol = wrl.io.open_rainbow_dataset(f, reindex_angle=False)
Downloading file 'rainbow/2013051000000600dBZ.vol' from 'https://github.com/wradlib/wradlib-data/raw/pooch/data/rainbow/2013051000000600dBZ.vol' to '/home/runner/work/wradlib-notebooks/wradlib-notebooks/wradlib-data'.
Inspect RadarVolume¶
[3]:
display(vol)
<wradlib.RadarVolume>
Dimension(s): (sweep: 14)
Elevation(s): (0.6, 1.4, 2.4, 3.5, 4.8, 6.3, 8.0, 9.9, 12.2, 14.8, 17.9, 21.3, 25.4, 30.0)
Inspect root group¶
The sweep dimension contains the number of scans in this radar volume. Further the dataset consists of variables (location coordinates, time_coverage) and attributes (Conventions, metadata).
[4]:
vol.root
[4]:
<xarray.Dataset>
Dimensions: (sweep: 14)
Dimensions without coordinates: sweep
Data variables:
volume_number int64 0
platform_type <U5 'fixed'
instrument_type <U5 'radar'
primary_axis <U6 'axis_z'
time_coverage_start <U20 '2013-05-10T00:00:06Z'
time_coverage_end <U20 '2013-05-10 00:03:15Z'
latitude float64 ...
longitude float64 ...
altitude float64 ...
sweep_group_name (sweep) <U8 'sweep_0' 'sweep_1' ... 'sweep_13'
sweep_fixed_angle (sweep) float64 0.6 1.4 2.4 3.5 ... 17.9 21.3 25.4 30.0
Attributes:
version: None
title: None
institution: None
references: None
source: None
history: None
comment: im/exported using wradlib
instrument_name: None
fixed_angle: 0.6Inspect sweep group(s)¶
The sweep-groups can be accessed via their respective keys. The dimensions consist of range and time with added coordinates azimuth, elevation, range and time. There will be variables like radar moments (DBZH etc.) and sweep-dependend metadata (like fixed_angle, sweep_mode etc.).
[5]:
display(vol[0])
<xarray.Dataset>
Dimensions: (azimuth: 361, range: 400)
Coordinates:
* azimuth (azimuth) float64 0.5492 1.505 2.549 ... 358.5 359.5
elevation (azimuth) float64 ...
* range (range) float32 125.0 375.0 625.0 ... 9.962e+04 9.988e+04
rtime (azimuth) datetime64[ns] 2013-05-10T00:00:15.530303500...
sweep_mode <U20 ...
longitude float64 ...
latitude float64 ...
altitude float64 ...
time datetime64[ns] 2013-05-10T00:00:06.015151500
Data variables:
DBZH (azimuth, range) float32 ...
sweep_number int64 ...
prt_mode <U7 ...
follow_mode <U7 ...
sweep_fixed_angle float64 0.6
Attributes:
fixed_angle: 0.6Goereferencing¶
[6]:
swp = vol[0].copy().pipe(wrl.georef.georeference_dataset)
Plotting¶
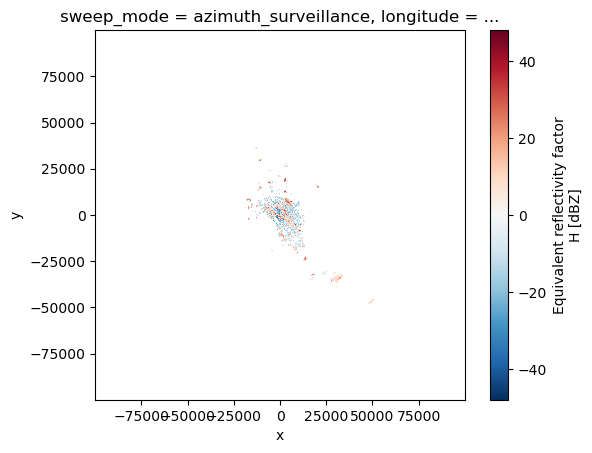
[7]:
swp.DBZH.plot.pcolormesh(x="x", y="y")
pl.gca().set_aspect("equal")
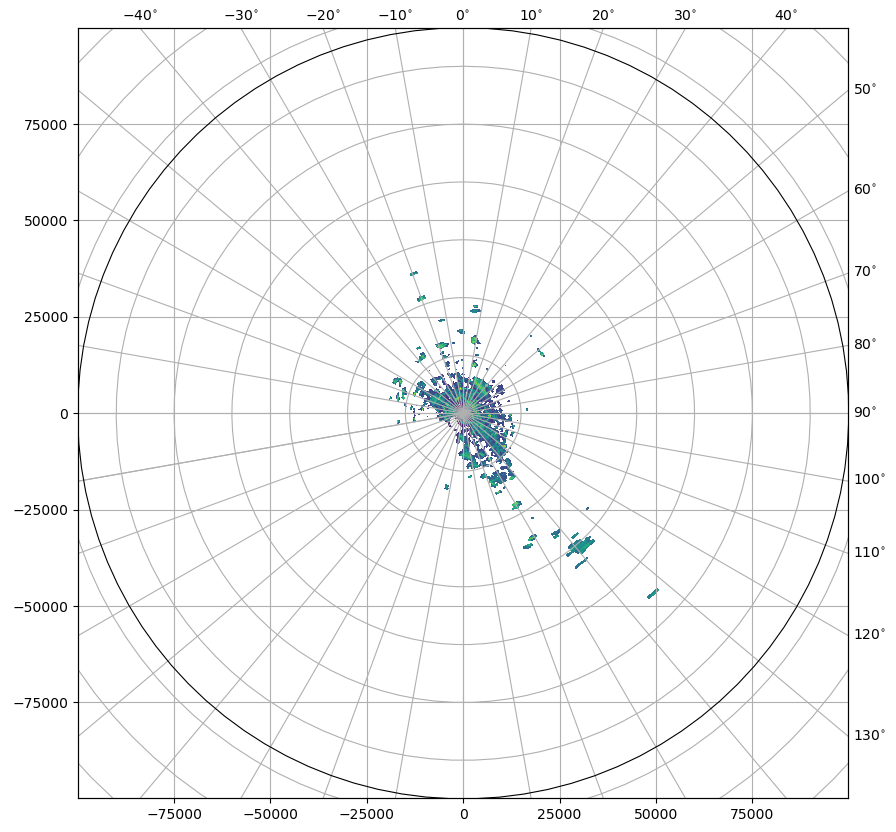
[8]:
fig = pl.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
swp.DBZH.wradlib.plot_ppi(proj="cg", fig=fig)
[8]:
<matplotlib.collections.QuadMesh at 0x7f05f2c52f50>
[9]:
import cartopy
import cartopy.crs as ccrs
import cartopy.feature as cfeature
map_trans = ccrs.AzimuthalEquidistant(
central_latitude=swp.latitude.values, central_longitude=swp.longitude.values
)
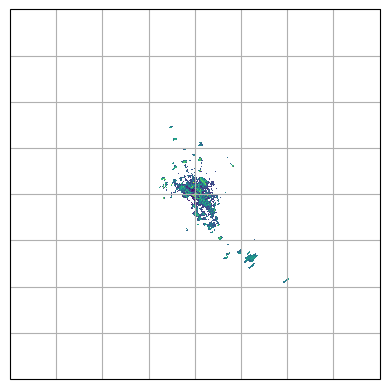
[10]:
map_proj = ccrs.AzimuthalEquidistant(
central_latitude=swp.latitude.values, central_longitude=swp.longitude.values
)
pm = swp.DBZH.wradlib.plot_ppi(proj=map_proj)
ax = pl.gca()
ax.gridlines(crs=map_proj)
print(ax)
< GeoAxes: +proj=aeqd +ellps=WGS84 +lon_0=6.379967 +lat_0=50.856633 +x_0=0.0 +y_0=0.0 +no_defs +type=crs >
[11]:
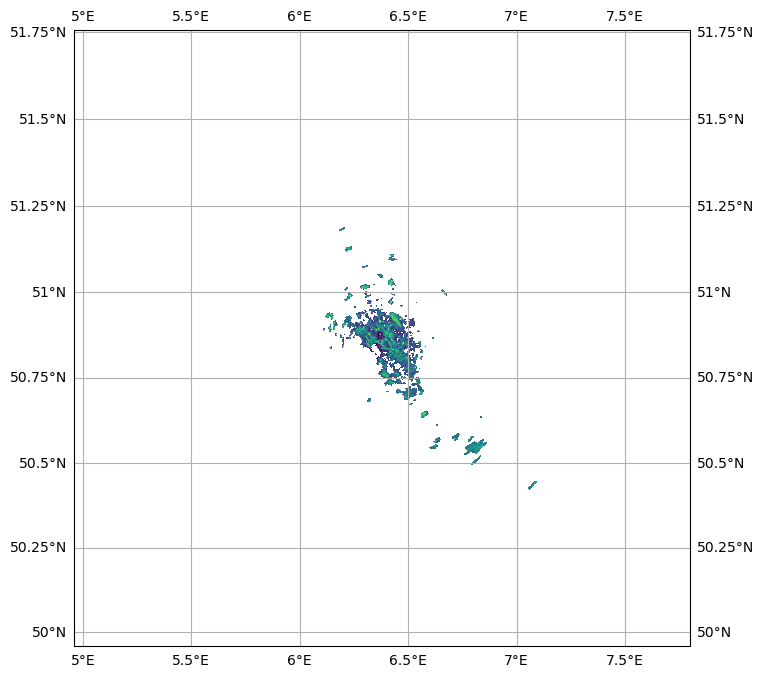
map_proj = ccrs.Mercator(central_longitude=swp.longitude.values)
fig = pl.figure(figsize=(10, 8))
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection=map_proj)
pm = swp.DBZH.wradlib.plot_ppi(ax=ax)
ax.gridlines(draw_labels=True)
[11]:
<cartopy.mpl.gridliner.Gridliner at 0x7f05f2bc7290>
[12]:
import cartopy.feature as cfeature
def plot_borders(ax):
borders = cfeature.NaturalEarthFeature(
category="physical", name="coastline", scale="10m", facecolor="none"
)
ax.add_feature(borders, edgecolor="black", lw=2, zorder=4)
map_proj = ccrs.Mercator(central_longitude=swp.longitude.values)
fig = pl.figure(figsize=(10, 8))
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection=map_proj)
DBZH = swp.DBZH
pm = DBZH.where(DBZH > 0).wradlib.plot_ppi(ax=ax)
plot_borders(ax)
ax.gridlines(draw_labels=True)
[12]:
<cartopy.mpl.gridliner.Gridliner at 0x7f05f2be48d0>
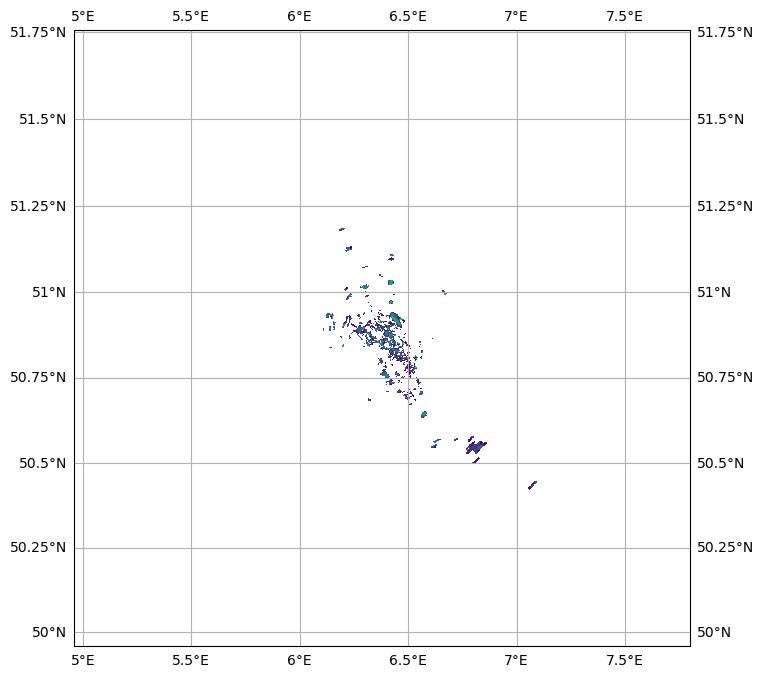
[13]:
import matplotlib.path as mpath
theta = np.linspace(0, 2 * np.pi, 100)
center, radius = [0.5, 0.5], 0.5
verts = np.vstack([np.sin(theta), np.cos(theta)]).T
circle = mpath.Path(verts * radius + center)
map_proj = ccrs.AzimuthalEquidistant(
central_latitude=swp.latitude.values,
central_longitude=swp.longitude.values,
)
fig = pl.figure(figsize=(10, 8))
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection=map_proj)
ax.set_boundary(circle, transform=ax.transAxes)
pm = swp.DBZH.wradlib.plot_ppi(proj=map_proj, ax=ax)
ax = pl.gca()
ax.gridlines(crs=map_proj)
[13]:
<cartopy.mpl.gridliner.Gridliner at 0x7f05ea9e7dd0>
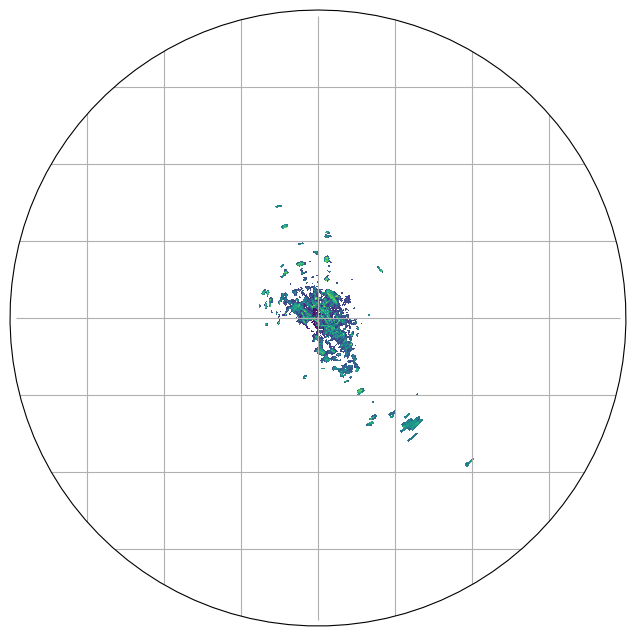
[14]:
fig = pl.figure(figsize=(10, 8))
proj = ccrs.AzimuthalEquidistant(
central_latitude=swp.latitude.values, central_longitude=swp.longitude.values
)
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection=proj)
pm = swp.DBZH.wradlib.plot_ppi(ax=ax)
ax.gridlines()
[14]:
<cartopy.mpl.gridliner.Gridliner at 0x7f05ea94fb10>
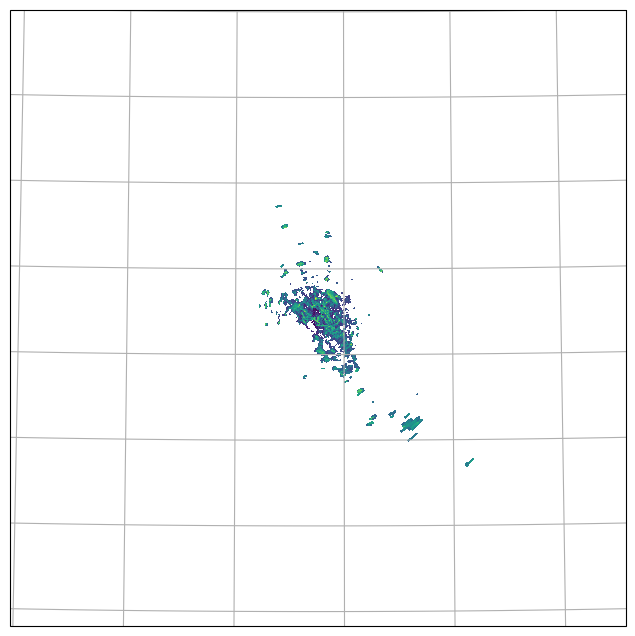
[15]:
swp.DBZH.wradlib.plot_ppi()
[15]:
<matplotlib.collections.QuadMesh at 0x7f05e867fc50>
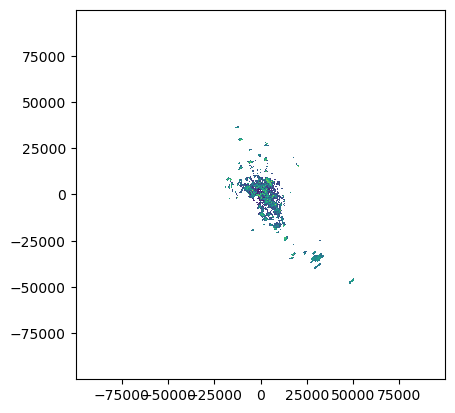
Inspect radar moments¶
The DataArrays can be accessed by key or by attribute. Each DataArray has dimensions and coordinates of it’s parent dataset.
[16]:
display(swp.DBZH)
<xarray.DataArray 'DBZH' (azimuth: 361, range: 400)>
array([[24.5, 21. , 1.5, ..., nan, nan, nan],
[25.5, 22.5, 0. , ..., nan, nan, nan],
[25.5, 22. , -3. , ..., nan, nan, nan],
...,
[24. , 30. , -5.5, ..., nan, nan, nan],
[25.5, 29.5, -5.5, ..., nan, nan, nan],
[24.5, 23. , 22. , ..., nan, nan, nan]], dtype=float32)
Coordinates: (12/15)
* azimuth (azimuth) float64 0.5492 1.505 2.549 3.516 ... 357.5 358.5 359.5
elevation (azimuth) float64 0.6 0.6 0.6 0.6 0.6 ... 0.6 0.6 0.6 0.6 0.6
* range (range) float32 125.0 375.0 625.0 ... 9.962e+04 9.988e+04
rtime (azimuth) datetime64[ns] 2013-05-10T00:00:15.530303500 ... 20...
sweep_mode <U20 'azimuth_surveillance'
longitude float64 6.38
... ...
x (azimuth, range) float64 1.198 3.594 5.99 ... -859.6 -861.8
y (azimuth, range) float64 125.0 375.0 ... 9.96e+04 9.985e+04
z (azimuth, range) float64 118.0 120.6 ... 1.744e+03 1.75e+03
gr (azimuth, range) float64 124.8 374.7 ... 9.96e+04 9.985e+04
rays (azimuth, range) float64 0.5492 0.5492 0.5492 ... 359.5 359.5
bins (azimuth, range) float32 125.0 375.0 ... 9.962e+04 9.988e+04
Attributes:
units: dBZ
standard_name: radar_equivalent_reflectivity_factor_h
long_name: Equivalent reflectivity factor HCreate simple plot¶
Using xarray features a simple plot can be created like this. Note the sortby('rtime') method, which sorts the radials by time.
[17]:
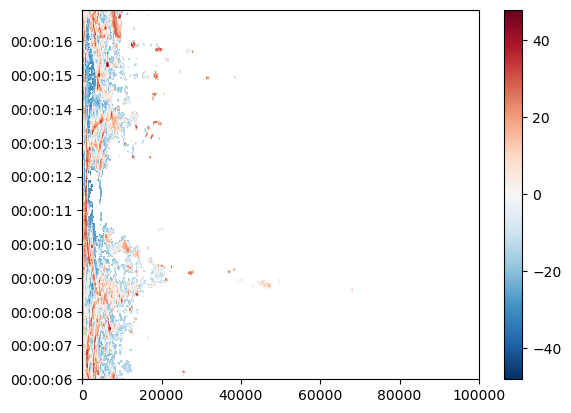
swp.DBZH.sortby("rtime").plot(x="range", y="rtime", add_labels=False)
[17]:
<matplotlib.collections.QuadMesh at 0x7f05e8669190>
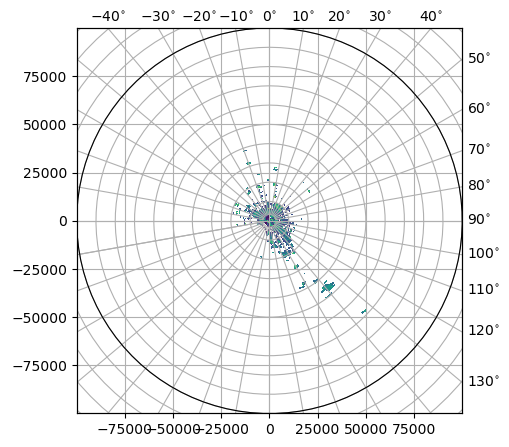
[18]:
fig = pl.figure(figsize=(5, 5))
pm = swp.DBZH.wradlib.plot_ppi(proj={"latmin": 3e3}, fig=fig)
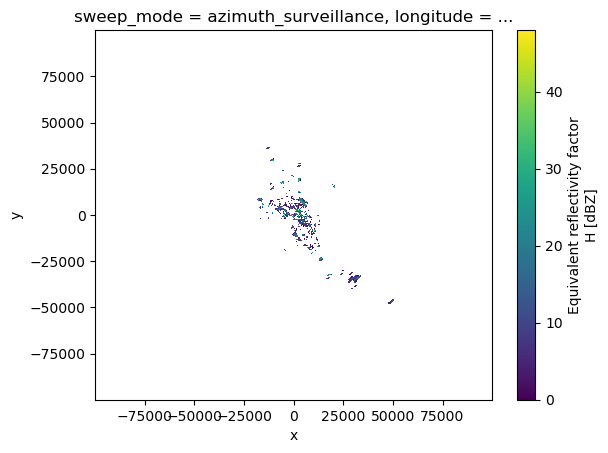
Mask some values¶
[19]:
dbzh = swp["DBZH"].where(swp["DBZH"] >= 0)
dbzh.plot(x="x", y="y")
[19]:
<matplotlib.collections.QuadMesh at 0x7f05e86c3c90>
[20]:
vol[0]
[20]:
<xarray.Dataset>
Dimensions: (azimuth: 361, range: 400)
Coordinates:
* azimuth (azimuth) float64 0.5492 1.505 2.549 ... 358.5 359.5
elevation (azimuth) float64 ...
* range (range) float32 125.0 375.0 625.0 ... 9.962e+04 9.988e+04
rtime (azimuth) datetime64[ns] 2013-05-10T00:00:15.530303500...
sweep_mode <U20 ...
longitude float64 ...
latitude float64 ...
altitude float64 ...
time datetime64[ns] 2013-05-10T00:00:06.015151500
Data variables:
DBZH (azimuth, range) float32 ...
sweep_number int64 ...
prt_mode <U7 ...
follow_mode <U7 ...
sweep_fixed_angle float64 0.6
Attributes:
fixed_angle: 0.6Export to ODIM and CfRadial2¶
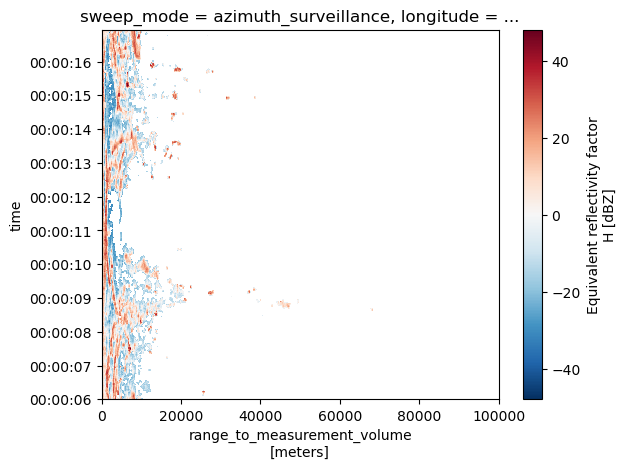
[21]:
vol[0].DBZH.sortby("rtime").plot(y="rtime")
[21]:
<matplotlib.collections.QuadMesh at 0x7f05e852af50>
[22]:
vol.to_odim("rainbow_as_odim.h5")
vol.to_cfradial2("rainbow_as_cfradial2.nc")
Import again¶
[23]:
vola = wrl.io.open_odim_dataset(
"rainbow_as_odim.h5", reindex_angle=False, keep_elevation=True
)
display(vola.root)
display(vola[0])
vola[0].DBZH.sortby("rtime").plot(y="rtime")
<xarray.Dataset>
Dimensions: (sweep: 14)
Dimensions without coordinates: sweep
Data variables:
volume_number int64 0
platform_type <U5 'fixed'
instrument_type <U5 'radar'
primary_axis <U6 'axis_z'
time_coverage_start <U20 '2013-05-10T00:00:06Z'
time_coverage_end <U20 '2013-05-10 00:03:15Z'
latitude float64 ...
longitude float64 ...
altitude float64 ...
sweep_group_name (sweep) <U8 'sweep_0' 'sweep_1' ... 'sweep_13'
sweep_fixed_angle (sweep) float64 0.6 1.4 2.4 3.5 ... 17.9 21.3 25.4 30.0
Attributes:
version: None
title: None
institution: None
references: None
source: None
history: None
comment: im/exported using wradlib
instrument_name: None
fixed_angle: 0.6<xarray.Dataset>
Dimensions: (azimuth: 361, range: 400)
Coordinates:
* azimuth (azimuth) float64 0.5492 1.505 2.549 ... 358.5 359.5
elevation (azimuth) float64 ...
rtime (azimuth) datetime64[ns] 2013-05-10T00:00:15.530303488...
* range (range) float32 125.0 375.0 625.0 ... 9.962e+04 9.988e+04
sweep_mode <U20 ...
longitude float64 ...
latitude float64 ...
altitude float64 ...
time datetime64[ns] 2013-05-10T00:00:06.015151616
Data variables:
DBZH (azimuth, range) float32 ...
sweep_number int64 ...
prt_mode <U7 ...
follow_mode <U7 ...
sweep_fixed_angle float64 0.6
Attributes:
fixed_angle: 0.6[23]:
<matplotlib.collections.QuadMesh at 0x7f05e84e1050>
[24]:
volb = wrl.io.open_cfradial2_dataset("rainbow_as_cfradial2.nc")
display(volb.root)
display(volb[0])
volb[0].DBZH.sortby("rtime").plot(y="rtime")
<xarray.Dataset>
Dimensions: (sweep: 14)
Dimensions without coordinates: sweep
Data variables:
volume_number int64 0
platform_type <U5 'fixed'
instrument_type <U5 'radar'
primary_axis <U6 'axis_z'
time_coverage_start <U20 '2013-05-10T00:00:06Z'
time_coverage_end <U20 '2013-05-10 00:03:15Z'
latitude float64 ...
longitude float64 ...
altitude float64 ...
sweep_group_name (sweep) <U8 'sweep_0' 'sweep_1' ... 'sweep_13'
sweep_fixed_angle (sweep) float64 0.6 1.4 2.4 3.5 ... 17.9 21.3 25.4 30.0
Attributes:
version: None
title: None
institution: None
references: None
source: None
history: None
comment: im/exported using wradlib
instrument_name: None
fixed_angle: 0.6<xarray.Dataset>
Dimensions: (azimuth: 361, range: 400)
Coordinates:
* azimuth (azimuth) float64 0.5492 1.505 2.549 ... 358.5 359.5
elevation (azimuth) float64 ...
* range (range) float32 125.0 375.0 625.0 ... 9.962e+04 9.988e+04
rtime (azimuth) datetime64[ns] 2013-05-10T00:00:15.530303500...
sweep_mode <U20 ...
longitude float64 ...
latitude float64 ...
altitude float64 ...
time datetime64[ns] 2013-05-10T00:00:06.015151500
Data variables:
DBZH (azimuth, range) float32 ...
sweep_number int64 ...
prt_mode object ...
follow_mode object ...
sweep_fixed_angle float64 0.6
Attributes:
fixed_angle: 0.6[24]:
<matplotlib.collections.QuadMesh at 0x7f05e2b05350>
Check equality¶
We have to sort accordingly and drop the time variables when checking equality.
[25]:
xr.testing.assert_allclose(vol.root, vola.root)
xr.testing.assert_allclose(
vol[0].drop(["rtime", "time"]), vola[0].drop(["rtime", "time"])
)
xr.testing.assert_allclose(vol.root, volb.root)
xr.testing.assert_allclose(
vol[0].drop(["rtime", "time"]), volb[0].drop(["rtime", "time"])
)
xr.testing.assert_allclose(vola.root, volb.root)
xr.testing.assert_allclose(
vola[0].drop(["rtime", "time"]), volb[0].drop(["rtime", "time"])
)
More Rainbow5 loading mechanisms¶
Use xr.open_dataset to retrieve explicit group¶
Warning
Since \(\omega radlib\) version 1.18 the xarray backend engines for polar radar data have been renamed and prepended with wradlib- (eg. rainbow -> wradlib-rainbow). This was necessary to avoid clashes with the new xradar-package, which will eventually replace the wradlib engines. Users have to make sure to check which engine to use for their use-case when using xarray.open_dataset. Users might install and test xradar, and check if
it is already robust enough for their use-cases (by using xradar’s engine="rainbow".
Since \(\omega radlib\) version 1.19 the xarray backend engines for polar radar data have been deprecated. The functionality is kept until wradlib version 2.0, when the backend-code will be removed completely. wradlib is importing that functionality from xradar-package whenever and wherever necessary.
Below we use a compatibility layer in wradlib to give users the chance to adapt their code. The first minimal change is that for every backend the group-layout is conforming to the CfRadial-standard naming scheme (sweep_0, sweep_1, etc.).
Below you can inspect the main differences of the wradlib compatibility layer and the plain xradar implementation.
use wradlib compatibility layer¶
[26]:
swp_a = xr.open_dataset(
f,
engine="wradlib-rainbow",
group="sweep_5",
backend_kwargs=dict(reindex_angle=False),
)
display(swp_a)
<xarray.Dataset>
Dimensions: (azimuth: 361, range: 400)
Coordinates:
* azimuth (azimuth) float64 0.5052 1.516 2.51 ... 357.5 358.5 359.5
elevation (azimuth) float64 ...
* range (range) float32 125.0 375.0 625.0 ... 9.962e+04 9.988e+04
rtime (azimuth) datetime64[ns] ...
sweep_mode <U20 ...
longitude float64 ...
latitude float64 ...
altitude float64 ...
time datetime64[ns] ...
Data variables:
DBZH (azimuth, range) float32 ...
sweep_number int64 ...
prt_mode <U7 ...
follow_mode <U7 ...
sweep_fixed_angle float64 ...
Attributes:
fixed_angle: 6.3use xradar-backend¶
[27]:
swp_b = xr.open_dataset(
f, engine="rainbow", group="sweep_5", backend_kwargs=dict(reindex_angle=False)
)
display(swp_b)
<xarray.Dataset>
Dimensions: (azimuth: 361, range: 400)
Coordinates:
* azimuth (azimuth) float64 0.5052 1.516 2.51 ... 357.5 358.5 359.5
elevation (azimuth) float64 ...
* range (range) float32 125.0 375.0 625.0 ... 9.962e+04 9.988e+04
time (azimuth) datetime64[ns] ...
longitude float64 ...
latitude float64 ...
altitude float64 ...
Data variables:
DBZH (azimuth, range) float32 ...
sweep_mode <U20 ...
sweep_number int64 ...
prt_mode <U7 ...
follow_mode <U7 ...
sweep_fixed_angle float64 ...[ ]: