Beam Blockage Calculation using a DEM¶
Here, we derive (partial) beam-blockage (PBB) from a Digital Elevation Model (DEM).
We require - the local radar setup (sitecoords, number of rays, number of bins, antenna elevation, beamwidth, and the range resolution); - a DEM with a adequate resolution.
Here we use pre-processed data from the GTOPO30 and SRTM missions.
[1]:
import wradlib as wrl
import matplotlib.pyplot as pl
import matplotlib as mpl
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
try:
get_ipython().run_line_magic("matplotlib inline")
except:
pl.ion()
import numpy as np
/home/runner/micromamba-root/envs/wradlib-notebooks/lib/python3.11/site-packages/tqdm/auto.py:22: TqdmWarning: IProgress not found. Please update jupyter and ipywidgets. See https://ipywidgets.readthedocs.io/en/stable/user_install.html
from .autonotebook import tqdm as notebook_tqdm
Setup for Bonn radar¶
First, we need to define some radar specifications (here: University of Bonn).
[2]:
sitecoords = (7.071663, 50.73052, 99.5)
nrays = 360 # number of rays
nbins = 1000 # number of range bins
el = 1.0 # vertical antenna pointing angle (deg)
bw = 1.0 # half power beam width (deg)
range_res = 100.0 # range resolution (meters)
Create the range, azimuth, and beamradius arrays.
[3]:
r = np.arange(nbins) * range_res
beamradius = wrl.util.half_power_radius(r, bw)
We use
to calculate the spherical coordinates of the bin centroids and their longitude, latitude and altitude.
[4]:
coord = wrl.georef.sweep_centroids(nrays, range_res, nbins, el)
coords = wrl.georef.spherical_to_proj(
coord[..., 0], coord[..., 1], coord[..., 2], sitecoords
)
lon = coords[..., 0]
lat = coords[..., 1]
alt = coords[..., 2]
[5]:
polcoords = coords[..., :2]
print("lon,lat,alt:", coords.shape)
lon,lat,alt: (360, 1000, 3)
[6]:
rlimits = (lon.min(), lat.min(), lon.max(), lat.max())
print(
"Radar bounding box:\n\t%.2f\n%.2f %.2f\n\t%.2f"
% (lat.max(), lon.min(), lon.max(), lat.min())
)
Radar bounding box:
51.63
5.66 8.49
49.83
Preprocessing the digitial elevation model¶
Read the DEM from a
geotifffile (inWRADLIB_DATA);clip the region inside the bounding box;
map the DEM values to the polar grid points.
Note: You can choose between the coarser resolution bonn_gtopo.tif (from GTOPO30) and the finer resolution bonn_new.tif (from the SRTM mission).
The DEM raster data is opened via wradlib.io.open_raster and extracted via wradlib.georef.extract_raster_dataset.
[7]:
# rasterfile = wrl.util.get_wradlib_data_file('geo/bonn_gtopo.tif')
rasterfile = wrl.util.get_wradlib_data_file("geo/bonn_new.tif")
ds = wrl.io.open_raster(rasterfile)
rastervalues, rastercoords, proj = wrl.georef.extract_raster_dataset(
ds, nodata=-32768.0
)
# Clip the region inside our bounding box
ind = wrl.util.find_bbox_indices(rastercoords, rlimits)
rastercoords = rastercoords[ind[1] : ind[3], ind[0] : ind[2], ...]
rastervalues = rastervalues[ind[1] : ind[3], ind[0] : ind[2]]
# Map rastervalues to polar grid points
polarvalues = wrl.ipol.cart_to_irregular_spline(
rastercoords, rastervalues, polcoords, order=3, prefilter=False
)
Downloading file 'geo/bonn_new.tif' from 'https://github.com/wradlib/wradlib-data/raw/pooch/data/geo/bonn_new.tif' to '/home/runner/work/wradlib-notebooks/wradlib-notebooks/wradlib-data'.
Calculate Beam-Blockage¶
Now we can finally apply the wradlib.qual.beam_block_frac function to calculate the PBB.
[8]:
PBB = wrl.qual.beam_block_frac(polarvalues, alt, beamradius)
PBB = np.ma.masked_invalid(PBB)
print(PBB.shape)
(360, 1000)
So far, we calculated the fraction of beam blockage for each bin.
But we need to into account that the radar signal travels along a beam. Cumulative beam blockage (CBB) in one bin along a beam will always be at least as high as the maximum PBB of the preceeding bins (see wradlib.qual.cum_beam_block_frac)
[9]:
CBB = wrl.qual.cum_beam_block_frac(PBB)
print(CBB.shape)
(360, 1000)
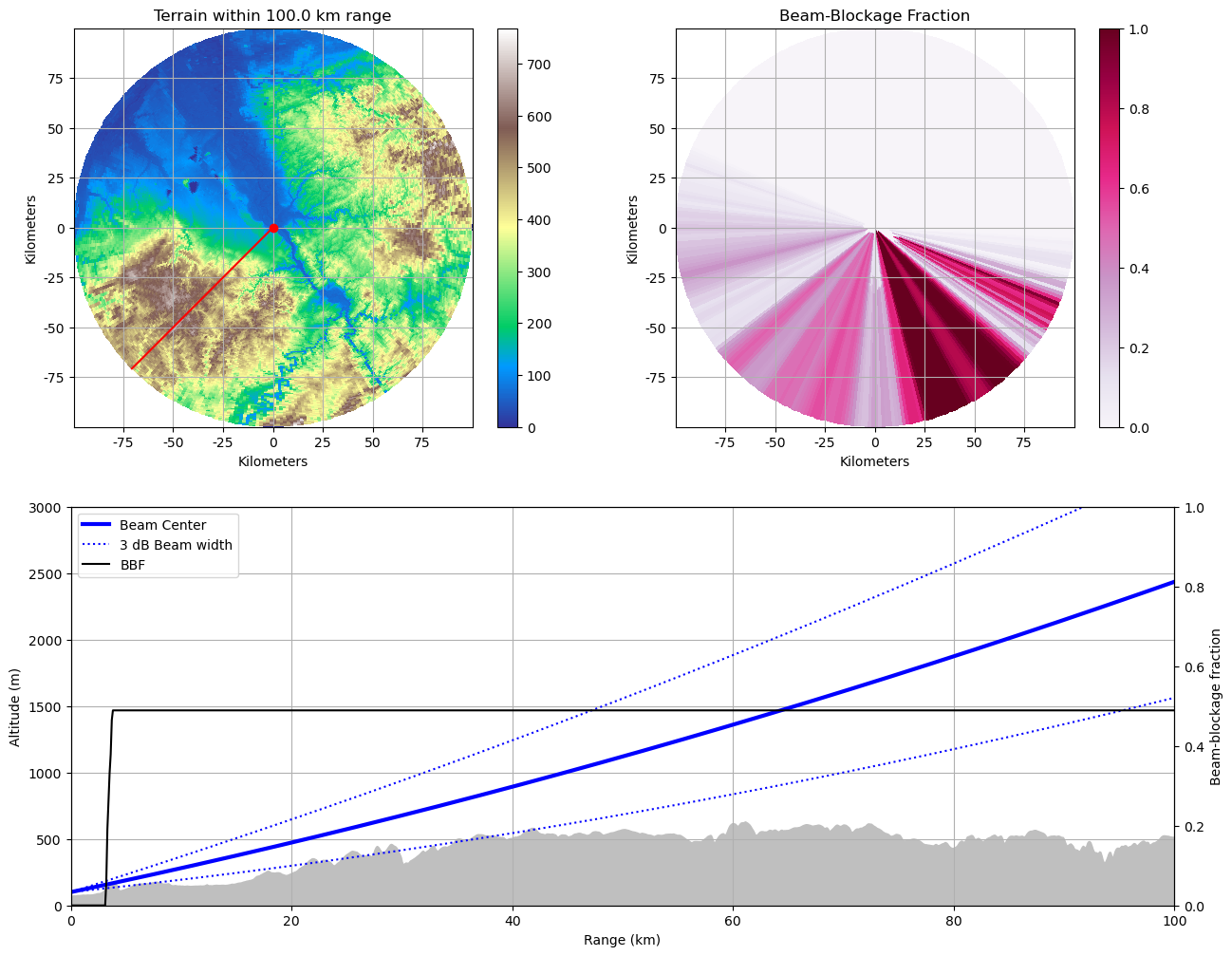
Visualize Beamblockage¶
Now we visualize - the average terrain altitude per radar bin - a beam blockage map - interaction with terrain along a single beam
[10]:
# just a little helper function to style x and y axes of our maps
def annotate_map(ax, cm=None, title=""):
ticks = (ax.get_xticks() / 1000).astype(int)
ax.set_xticklabels(ticks)
ticks = (ax.get_yticks() / 1000).astype(int)
ax.set_yticklabels(ticks)
ax.set_xlabel("Kilometers")
ax.set_ylabel("Kilometers")
if not cm is None:
pl.colorbar(cm, ax=ax)
if not title == "":
ax.set_title(title)
ax.grid()
[11]:
fig = pl.figure(figsize=(15, 12))
# create subplots
ax1 = pl.subplot2grid((2, 2), (0, 0))
ax2 = pl.subplot2grid((2, 2), (0, 1))
ax3 = pl.subplot2grid((2, 2), (1, 0), colspan=2, rowspan=1)
# azimuth angle
angle = 225
# Plot terrain (on ax1)
ax1, dem = wrl.vis.plot_ppi(
polarvalues, ax=ax1, r=r, az=coord[:, 0, 1], cmap=mpl.cm.terrain, vmin=0.0
)
ax1.plot(
[0, np.sin(np.radians(angle)) * 1e5], [0, np.cos(np.radians(angle)) * 1e5], "r-"
)
ax1.plot(sitecoords[0], sitecoords[1], "ro")
annotate_map(ax1, dem, "Terrain within {0} km range".format(np.max(r / 1000.0) + 0.1))
# Plot CBB (on ax2)
ax2, cbb = wrl.vis.plot_ppi(
CBB, ax=ax2, r=r, az=coord[:, 0, 1], cmap=mpl.cm.PuRd, vmin=0, vmax=1
)
annotate_map(ax2, cbb, "Beam-Blockage Fraction")
# Plot single ray terrain profile on ax3
(bc,) = ax3.plot(r / 1000.0, alt[angle, :], "-b", linewidth=3, label="Beam Center")
(b3db,) = ax3.plot(
r / 1000.0,
(alt[angle, :] + beamradius),
":b",
linewidth=1.5,
label="3 dB Beam width",
)
ax3.plot(r / 1000.0, (alt[angle, :] - beamradius), ":b")
ax3.fill_between(r / 1000.0, 0.0, polarvalues[angle, :], color="0.75")
ax3.set_xlim(0.0, np.max(r / 1000.0) + 0.1)
ax3.set_ylim(0.0, 3000)
ax3.set_xlabel("Range (km)")
ax3.set_ylabel("Altitude (m)")
ax3.grid()
axb = ax3.twinx()
(bbf,) = axb.plot(r / 1000.0, CBB[angle, :], "-k", label="BBF")
axb.set_ylabel("Beam-blockage fraction")
axb.set_ylim(0.0, 1.0)
axb.set_xlim(0.0, np.max(r / 1000.0) + 0.1)
legend = ax3.legend(
(bc, b3db, bbf),
("Beam Center", "3 dB Beam width", "BBF"),
loc="upper left",
fontsize=10,
)
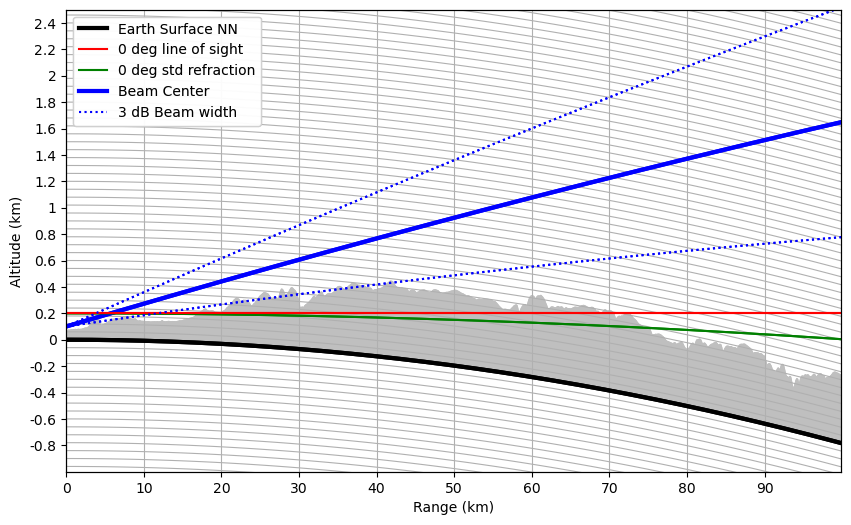
Visualize Beam Propagation showing earth curvature¶
Now we visualize - interaction with terrain along a single beam
In this representation the earth curvature is shown. For this we assume the earth a sphere with exactly 6370000 m radius. This is needed to get the height ticks at nice position.
[12]:
def height_formatter(x, pos):
x = (x - 6370000) / 1000
fmt_str = "{:g}".format(x)
return fmt_str
def range_formatter(x, pos):
x = x / 1000.0
fmt_str = "{:g}".format(x)
return fmt_str
The wradlib.vis.create_cg-function is facilitated to create the curved geometries.
The actual data is plottet as (theta, range) on the parasite axis.
Some tweaking is needed to get the final plot look nice.
[13]:
fig = pl.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
cgax, caax, paax = wrl.vis.create_cg(fig=fig, rot=0, scale=1)
# azimuth angle
angle = 225
# fix grid_helper
er = 6370000
gh = cgax.get_grid_helper()
gh.grid_finder.grid_locator2._nbins = 80
gh.grid_finder.grid_locator2._steps = [1, 2, 4, 5, 10]
# calculate beam_height and arc_distance for ke=1
# means line of sight
bhe = wrl.georef.bin_altitude(r, 0, sitecoords[2], re=er, ke=1.0)
ade = wrl.georef.bin_distance(r, 0, sitecoords[2], re=er, ke=1.0)
nn0 = np.zeros_like(r)
# for nice plotting we assume earth_radius = 6370000 m
ecp = nn0 + er
# theta (arc_distance sector angle)
thetap = -np.degrees(ade / er) + 90.0
# zero degree elevation with standard refraction
bh0 = wrl.georef.bin_altitude(r, 0, sitecoords[2], re=er)
# plot (ecp is earth surface normal null)
(bes,) = paax.plot(thetap, ecp, "-k", linewidth=3, label="Earth Surface NN")
(bc,) = paax.plot(thetap, ecp + alt[angle, :], "-b", linewidth=3, label="Beam Center")
(bc0r,) = paax.plot(thetap, ecp + bh0 + alt[angle, 0], "-g", label="0 deg Refraction")
(bc0n,) = paax.plot(
thetap, ecp + bhe + alt[angle, 0], "-r", label="0 deg line of sight"
)
(b3db,) = paax.plot(
thetap, ecp + alt[angle, :] + beamradius, ":b", label="+3 dB Beam width"
)
paax.plot(thetap, ecp + alt[angle, :] - beamradius, ":b", label="-3 dB Beam width")
# orography
paax.fill_between(thetap, ecp, ecp + polarvalues[angle, :], color="0.75")
# shape axes
cgax.set_xlim(0, np.max(ade))
cgax.set_ylim([ecp.min() - 1000, ecp.max() + 2500])
caax.grid(True, axis="x")
cgax.grid(True, axis="y")
cgax.axis["top"].toggle(all=False)
caax.yaxis.set_major_locator(
mpl.ticker.MaxNLocator(steps=[1, 2, 4, 5, 10], nbins=20, prune="both")
)
caax.xaxis.set_major_locator(mpl.ticker.MaxNLocator())
caax.yaxis.set_major_formatter(mpl.ticker.FuncFormatter(height_formatter))
caax.xaxis.set_major_formatter(mpl.ticker.FuncFormatter(range_formatter))
caax.set_xlabel("Range (km)")
caax.set_ylabel("Altitude (km)")
legend = paax.legend(
(bes, bc0n, bc0r, bc, b3db),
(
"Earth Surface NN",
"0 deg line of sight",
"0 deg std refraction",
"Beam Center",
"3 dB Beam width",
),
loc="upper left",
fontsize=10,
)
Go back to Read DEM Raster Data, change the rasterfile to use the other resolution DEM and process again.